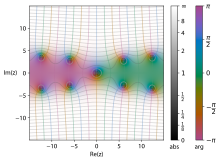
Plot of the hyperbolic sine integral function Shi(z ) in the complex plane from −2 − 2i to 2 + 2i
Special function defined by an integral
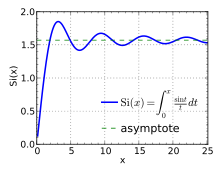
Si(x ) (blue) and Ci(x ) (green) shown on the same plot.Sine integral in the complex plane, plotted with a variant of domain coloring . branch cut along the negative real axis.In mathematics , trigonometric integrals are a family of nonelementary integrals involving trigonometric functions .
Plot of Si(x ) for 0 ≤ x ≤ 8π . Plot of the cosine integral function Ci(z ) in the complex plane from −2 − 2i to 2 + 2i The different sine integral definitions are
Si
(
x
)
=
∫
0
x
sin
t
t
d
t
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (x)=\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {\sin t}{t}}\,dt}
si
(
x
)
=
−
∫
x
∞
sin
t
t
d
t
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {si} (x)=-\int _{x}^{\infty }{\frac {\sin t}{t}}\,dt~.}
Note that the integrand
sin
(
t
)
t
{\displaystyle {\frac {\sin(t)}{t}}}
sinc function , and also the zeroth spherical Bessel function .
Since sinc is an even entire function (holomorphic over the entire complex plane), Si is entire, odd, and the integral in its definition can be taken along any path connecting the endpoints.
By definition, Si(x ) is the antiderivative of sin x / x whose value is zero at x = 0si(x ) is the antiderivative whose value is zero at x = ∞Dirichlet integral ,
Si
(
x
)
−
si
(
x
)
=
∫
0
∞
sin
t
t
d
t
=
π
2
or
Si
(
x
)
=
π
2
+
si
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (x)-\operatorname {si} (x)=\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {\sin t}{t}}\,dt={\frac {\pi }{2}}\quad {\text{ or }}\quad \operatorname {Si} (x)={\frac {\pi }{2}}+\operatorname {si} (x)~.}
In signal processing , the oscillations of the sine integral cause overshoot and ringing artifacts when using the sinc filter , and frequency domain ringing if using a truncated sinc filter as a low-pass filter .
Related is the Gibbs phenomenon : If the sine integral is considered as the convolution of the sinc function with the Heaviside step function , this corresponds to truncating the Fourier series , which is the cause of the Gibbs phenomenon.
Plot of Ci(x ) for 0 < x ≤ 8π The different cosine integral definitions are
Cin
(
x
)
≡
∫
0
x
1
−
cos
t
t
d
t
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Cin} (x)~\equiv ~\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {\ 1-\cos t\ }{t}}\ \operatorname {d} t~.}
Cin is an even , entire function . For that reason, some texts define Cin as the primary function, and derive Ci in terms of Cin .
Ci
(
x
)
≡
−
∫
x
∞
cos
t
t
d
t
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Ci} (x)~~\equiv ~-\int _{x}^{\infty }{\frac {\ \cos t\ }{t}}\ \operatorname {d} t~}
=
γ
+
ln
x
−
∫
0
x
1
−
cos
t
t
d
t
{\displaystyle ~~\qquad ~=~~\gamma ~+~\ln x~-~\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {\ 1-\cos t\ }{t}}\ \operatorname {d} t~}
=
γ
+
ln
x
−
Cin
x
{\displaystyle ~~\qquad ~=~~\gamma ~+~\ln x~-~\operatorname {Cin} x~}
|
Arg
(
x
)
|
<
π
,
{\displaystyle ~{\Bigl |}\ \operatorname {Arg} (x)\ {\Bigr |}<\pi \ ,}
γ ≈ 0.57721566490 ... is the Euler–Mascheroni constant . Some texts use ci instead of Ci . The restriction on Arg(x) is to avoid a discontinuity (shown as the orange vs blue area on the left half of the plot above ) that arises because of a branch cut in the standard logarithm function ( ln ).
Ci(x ) is the antiderivative of cos x / x (which vanishes as
x
→
∞
{\displaystyle \ x\to \infty \ }
Ci
(
x
)
=
γ
+
ln
x
−
Cin
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Ci} (x)=\gamma +\ln x-\operatorname {Cin} (x)~.}
Hyperbolic sine integral [ edit ] The hyperbolic sine integral is defined as
Shi
(
x
)
=
∫
0
x
sinh
(
t
)
t
d
t
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Shi} (x)=\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {\sinh(t)}{t}}\,dt.}
It is related to the ordinary sine integral by
Si
(
i
x
)
=
i
Shi
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (ix)=i\operatorname {Shi} (x).}
Hyperbolic cosine integral [ edit ] The hyperbolic cosine integral is
Plot of the hyperbolic cosine integral function Chi(z ) in the complex plane from −2 − 2i to 2 + 2i
Chi
(
x
)
=
γ
+
ln
x
+
∫
0
x
cosh
t
−
1
t
d
t
for
|
Arg
(
x
)
|
<
π
,
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Chi} (x)=\gamma +\ln x+\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {\cosh t-1}{t}}\,dt\qquad ~{\text{ for }}~\left|\operatorname {Arg} (x)\right|<\pi ~,}
γ
{\displaystyle \gamma }
Euler–Mascheroni constant .
It has the series expansion
Chi
(
x
)
=
γ
+
ln
(
x
)
+
x
2
4
+
x
4
96
+
x
6
4320
+
x
8
322560
+
x
10
36288000
+
O
(
x
12
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Chi} (x)=\gamma +\ln(x)+{\frac {x^{2}}{4}}+{\frac {x^{4}}{96}}+{\frac {x^{6}}{4320}}+{\frac {x^{8}}{322560}}+{\frac {x^{10}}{36288000}}+O(x^{12}).}
Auxiliary functions [ edit ] Trigonometric integrals can be understood in terms of the so-called "auxiliary functions "
f
(
x
)
≡
∫
0
∞
sin
(
t
)
t
+
x
d
t
=
∫
0
∞
e
−
x
t
t
2
+
1
d
t
=
Ci
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
+
[
π
2
−
Si
(
x
)
]
cos
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
≡
∫
0
∞
cos
(
t
)
t
+
x
d
t
=
∫
0
∞
t
e
−
x
t
t
2
+
1
d
t
=
−
Ci
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
+
[
π
2
−
Si
(
x
)
]
sin
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{array}{rcl}f(x)&\equiv &\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {\sin(t)}{t+x}}\,dt&=&\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {e^{-xt}}{t^{2}+1}}\,dt&=&\operatorname {Ci} (x)\sin(x)+\left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\cos(x)~,\\g(x)&\equiv &\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {\cos(t)}{t+x}}\,dt&=&\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {te^{-xt}}{t^{2}+1}}\,dt&=&-\operatorname {Ci} (x)\cos(x)+\left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\sin(x)~.\end{array}}}
p. 232 )
π
2
−
Si
(
x
)
=
−
si
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
,
and
Ci
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
−
g
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{array}{rcl}{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)=-\operatorname {si} (x)&=&f(x)\cos(x)+g(x)\sin(x)~,\qquad {\text{ and }}\\\operatorname {Ci} (x)&=&f(x)\sin(x)-g(x)\cos(x)~.\\\end{array}}}
Nielsen's spiral. The spiral formed by parametric plot of si, ci is known as Nielsen's spiral.
x
(
t
)
=
a
×
ci
(
t
)
{\displaystyle x(t)=a\times \operatorname {ci} (t)}
y
(
t
)
=
a
×
si
(
t
)
{\displaystyle y(t)=a\times \operatorname {si} (t)}
The spiral is closely related to the Fresnel integrals and the Euler spiral . Nielsen's spiral has applications in vision processing, road and track construction and other areas.[ 1]
Various expansions can be used for evaluation of trigonometric integrals, depending on the range of the argument.
[ edit ]
Si
(
x
)
∼
π
2
−
cos
x
x
(
1
−
2
!
x
2
+
4
!
x
4
−
6
!
x
6
⋯
)
−
sin
x
x
(
1
x
−
3
!
x
3
+
5
!
x
5
−
7
!
x
7
⋯
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (x)\sim {\frac {\pi }{2}}-{\frac {\cos x}{x}}\left(1-{\frac {2!}{x^{2}}}+{\frac {4!}{x^{4}}}-{\frac {6!}{x^{6}}}\cdots \right)-{\frac {\sin x}{x}}\left({\frac {1}{x}}-{\frac {3!}{x^{3}}}+{\frac {5!}{x^{5}}}-{\frac {7!}{x^{7}}}\cdots \right)}
Ci
(
x
)
∼
sin
x
x
(
1
−
2
!
x
2
+
4
!
x
4
−
6
!
x
6
⋯
)
−
cos
x
x
(
1
x
−
3
!
x
3
+
5
!
x
5
−
7
!
x
7
⋯
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Ci} (x)\sim {\frac {\sin x}{x}}\left(1-{\frac {2!}{x^{2}}}+{\frac {4!}{x^{4}}}-{\frac {6!}{x^{6}}}\cdots \right)-{\frac {\cos x}{x}}\left({\frac {1}{x}}-{\frac {3!}{x^{3}}}+{\frac {5!}{x^{5}}}-{\frac {7!}{x^{7}}}\cdots \right)~.}
These series are asymptotic and divergent, although can be used for estimates and even precise evaluation at ℜ(x ) ≫ 1 .
Si
(
x
)
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
(
−
1
)
n
x
2
n
+
1
(
2
n
+
1
)
(
2
n
+
1
)
!
=
x
−
x
3
3
!
⋅
3
+
x
5
5
!
⋅
5
−
x
7
7
!
⋅
7
±
⋯
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (x)=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{n}x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)(2n+1)!}}=x-{\frac {x^{3}}{3!\cdot 3}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!\cdot 5}}-{\frac {x^{7}}{7!\cdot 7}}\pm \cdots }
Ci
(
x
)
=
γ
+
ln
x
+
∑
n
=
1
∞
(
−
1
)
n
x
2
n
2
n
(
2
n
)
!
=
γ
+
ln
x
−
x
2
2
!
⋅
2
+
x
4
4
!
⋅
4
∓
⋯
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Ci} (x)=\gamma +\ln x+\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{n}x^{2n}}{2n(2n)!}}=\gamma +\ln x-{\frac {x^{2}}{2!\cdot 2}}+{\frac {x^{4}}{4!\cdot 4}}\mp \cdots }
These series are convergent at any complex x , although for |x , the series will converge slowly initially, requiring many terms for high precision.
Derivation of series expansion [ edit ] From the Maclaurin series expansion of sine:
sin
x
=
x
−
x
3
3
!
+
x
5
5
!
−
x
7
7
!
+
x
9
9
!
−
x
11
11
!
+
⋯
{\displaystyle \sin \,x=x-{\frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!}}-{\frac {x^{7}}{7!}}+{\frac {x^{9}}{9!}}-{\frac {x^{11}}{11!}}+\cdots }
sin
x
x
=
1
−
x
2
3
!
+
x
4
5
!
−
x
6
7
!
+
x
8
9
!
−
x
10
11
!
+
⋯
{\displaystyle {\frac {\sin \,x}{x}}=1-{\frac {x^{2}}{3!}}+{\frac {x^{4}}{5!}}-{\frac {x^{6}}{7!}}+{\frac {x^{8}}{9!}}-{\frac {x^{10}}{11!}}+\cdots }
∴
∫
sin
x
x
d
x
=
x
−
x
3
3
!
⋅
3
+
x
5
5
!
⋅
5
−
x
7
7
!
⋅
7
+
x
9
9
!
⋅
9
−
x
11
11
!
⋅
11
+
⋯
{\displaystyle \therefore \int {\frac {\sin \,x}{x}}dx=x-{\frac {x^{3}}{3!\cdot 3}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!\cdot 5}}-{\frac {x^{7}}{7!\cdot 7}}+{\frac {x^{9}}{9!\cdot 9}}-{\frac {x^{11}}{11!\cdot 11}}+\cdots }
Relation with the exponential integral of imaginary argument [ edit ] The function
E
1
(
z
)
=
∫
1
∞
exp
(
−
z
t
)
t
d
t
for
ℜ
(
z
)
≥
0
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} _{1}(z)=\int _{1}^{\infty }{\frac {\exp(-zt)}{t}}\,dt\qquad ~{\text{ for }}~\Re (z)\geq 0}
exponential integral . It is closely related to Si and Ci ,
E
1
(
i
x
)
=
i
(
−
π
2
+
Si
(
x
)
)
−
Ci
(
x
)
=
i
si
(
x
)
−
ci
(
x
)
for
x
>
0
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} _{1}(ix)=i\left(-{\frac {\pi }{2}}+\operatorname {Si} (x)\right)-\operatorname {Ci} (x)=i\operatorname {si} (x)-\operatorname {ci} (x)\qquad ~{\text{ for }}~x>0~.}
As each respective function is analytic except for the cut at negative values of the argument, the area of validity of the relation should be extended to (Outside this range, additional terms which are integer factors of π
Cases of imaginary argument of the generalized integro-exponential function are
∫
1
∞
cos
(
a
x
)
ln
x
x
d
x
=
−
π
2
24
+
γ
(
γ
2
+
ln
a
)
+
ln
2
a
2
+
∑
n
≥
1
(
−
a
2
)
n
(
2
n
)
!
(
2
n
)
2
,
{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{\infty }\cos(ax){\frac {\ln x}{x}}\,dx=-{\frac {\pi ^{2}}{24}}+\gamma \left({\frac {\gamma }{2}}+\ln a\right)+{\frac {\ln ^{2}a}{2}}+\sum _{n\geq 1}{\frac {(-a^{2})^{n}}{(2n)!(2n)^{2}}}~,}
∫
1
∞
e
i
a
x
ln
x
x
d
x
=
−
π
2
24
+
γ
(
γ
2
+
ln
a
)
+
ln
2
a
2
−
π
2
i
(
γ
+
ln
a
)
+
∑
n
≥
1
(
i
a
)
n
n
!
n
2
.
{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{\infty }e^{iax}{\frac {\ln x}{x}}\,dx=-{\frac {\pi ^{2}}{24}}+\gamma \left({\frac {\gamma }{2}}+\ln a\right)+{\frac {\ln ^{2}a}{2}}-{\frac {\pi }{2}}i\left(\gamma +\ln a\right)+\sum _{n\geq 1}{\frac {(ia)^{n}}{n!n^{2}}}~.}
Similarly
∫
1
∞
e
i
a
x
ln
x
x
2
d
x
=
1
+
i
a
[
−
π
2
24
+
γ
(
γ
2
+
ln
a
−
1
)
+
ln
2
a
2
−
ln
a
+
1
]
+
π
a
2
(
γ
+
ln
a
−
1
)
+
∑
n
≥
1
(
i
a
)
n
+
1
(
n
+
1
)
!
n
2
.
{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{\infty }e^{iax}{\frac {\ln x}{x^{2}}}\,dx=1+ia\left[-{\frac {\pi ^{2}}{24}}+\gamma \left({\frac {\gamma }{2}}+\ln a-1\right)+{\frac {\ln ^{2}a}{2}}-\ln a+1\right]+{\frac {\pi a}{2}}{\Bigl (}\gamma +\ln a-1{\Bigr )}+\sum _{n\geq 1}{\frac {(ia)^{n+1}}{(n+1)!n^{2}}}~.}
Efficient evaluation [ edit ] Padé approximants of the convergent Taylor series provide an efficient way to evaluate the functions for small arguments. The following formulae, given by Rowe et al. (2015),[ 2] 10−16 for 0 ≤ x ≤ 4 ,
Si
(
x
)
≈
x
⋅
(
1
−
4.54393409816329991
⋅
10
−
2
⋅
x
2
+
1.15457225751016682
⋅
10
−
3
⋅
x
4
−
1.41018536821330254
⋅
10
−
5
⋅
x
6
+
9.43280809438713025
⋅
10
−
8
⋅
x
8
−
3.53201978997168357
⋅
10
−
10
⋅
x
10
+
7.08240282274875911
⋅
10
−
13
⋅
x
12
−
6.05338212010422477
⋅
10
−
16
⋅
x
14
1
+
1.01162145739225565
⋅
10
−
2
⋅
x
2
+
4.99175116169755106
⋅
10
−
5
⋅
x
4
+
1.55654986308745614
⋅
10
−
7
⋅
x
6
+
3.28067571055789734
⋅
10
−
10
⋅
x
8
+
4.5049097575386581
⋅
10
−
13
⋅
x
10
+
3.21107051193712168
⋅
10
−
16
⋅
x
12
)
Ci
(
x
)
≈
γ
+
ln
(
x
)
+
x
2
⋅
(
−
0.25
+
7.51851524438898291
⋅
10
−
3
⋅
x
2
−
1.27528342240267686
⋅
10
−
4
⋅
x
4
+
1.05297363846239184
⋅
10
−
6
⋅
x
6
−
4.68889508144848019
⋅
10
−
9
⋅
x
8
+
1.06480802891189243
⋅
10
−
11
⋅
x
10
−
9.93728488857585407
⋅
10
−
15
⋅
x
12
1
+
1.1592605689110735
⋅
10
−
2
⋅
x
2
+
6.72126800814254432
⋅
10
−
5
⋅
x
4
+
2.55533277086129636
⋅
10
−
7
⋅
x
6
+
6.97071295760958946
⋅
10
−
10
⋅
x
8
+
1.38536352772778619
⋅
10
−
12
⋅
x
10
+
1.89106054713059759
⋅
10
−
15
⋅
x
12
+
1.39759616731376855
⋅
10
−
18
⋅
x
14
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{array}{rcl}\operatorname {Si} (x)&\approx &x\cdot \left({\frac {\begin{array}{l}1-4.54393409816329991\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot x^{2}+1.15457225751016682\cdot 10^{-3}\cdot x^{4}-1.41018536821330254\cdot 10^{-5}\cdot x^{6}\\~~~+9.43280809438713025\cdot 10^{-8}\cdot x^{8}-3.53201978997168357\cdot 10^{-10}\cdot x^{10}+7.08240282274875911\cdot 10^{-13}\cdot x^{12}\\~~~-6.05338212010422477\cdot 10^{-16}\cdot x^{14}\end{array}}{\begin{array}{l}1+1.01162145739225565\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot x^{2}+4.99175116169755106\cdot 10^{-5}\cdot x^{4}+1.55654986308745614\cdot 10^{-7}\cdot x^{6}\\~~~+3.28067571055789734\cdot 10^{-10}\cdot x^{8}+4.5049097575386581\cdot 10^{-13}\cdot x^{10}+3.21107051193712168\cdot 10^{-16}\cdot x^{12}\end{array}}}\right)\\&~&\\\operatorname {Ci} (x)&\approx &\gamma +\ln(x)+\\&&x^{2}\cdot \left({\frac {\begin{array}{l}-0.25+7.51851524438898291\cdot 10^{-3}\cdot x^{2}-1.27528342240267686\cdot 10^{-4}\cdot x^{4}+1.05297363846239184\cdot 10^{-6}\cdot x^{6}\\~~~-4.68889508144848019\cdot 10^{-9}\cdot x^{8}+1.06480802891189243\cdot 10^{-11}\cdot x^{10}-9.93728488857585407\cdot 10^{-15}\cdot x^{12}\\\end{array}}{\begin{array}{l}1+1.1592605689110735\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot x^{2}+6.72126800814254432\cdot 10^{-5}\cdot x^{4}+2.55533277086129636\cdot 10^{-7}\cdot x^{6}\\~~~+6.97071295760958946\cdot 10^{-10}\cdot x^{8}+1.38536352772778619\cdot 10^{-12}\cdot x^{10}+1.89106054713059759\cdot 10^{-15}\cdot x^{12}\\~~~+1.39759616731376855\cdot 10^{-18}\cdot x^{14}\\\end{array}}}\right)\end{array}}}
The integrals may be evaluated indirectly via auxiliary functions
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle f(x)}
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle g(x)}
Si
(
x
)
=
π
2
−
f
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
−
g
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Si} (x)={\frac {\pi }{2}}-f(x)\cos(x)-g(x)\sin(x)}
Ci
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
−
g
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Ci} (x)=f(x)\sin(x)-g(x)\cos(x)}
or equivalently
f
(
x
)
≡
[
π
2
−
Si
(
x
)
]
cos
(
x
)
+
Ci
(
x
)
sin
(
x
)
{\displaystyle f(x)\equiv \left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\cos(x)+\operatorname {Ci} (x)\sin(x)}
g
(
x
)
≡
[
π
2
−
Si
(
x
)
]
sin
(
x
)
−
Ci
(
x
)
cos
(
x
)
{\displaystyle g(x)\equiv \left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\sin(x)-\operatorname {Ci} (x)\cos(x)}
For
x
≥
4
{\displaystyle x\geq 4}
Padé rational functions given below approximate
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle f(x)}
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle g(x)}
−16 :[ 2]
f
(
x
)
≈
1
x
⋅
(
1
+
7.44437068161936700618
⋅
10
2
⋅
x
−
2
+
1.96396372895146869801
⋅
10
5
⋅
x
−
4
+
2.37750310125431834034
⋅
10
7
⋅
x
−
6
+
1.43073403821274636888
⋅
10
9
⋅
x
−
8
+
4.33736238870432522765
⋅
10
10
⋅
x
−
10
+
6.40533830574022022911
⋅
10
11
⋅
x
−
12
+
4.20968180571076940208
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
14
+
1.00795182980368574617
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
16
+
4.94816688199951963482
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
18
−
4.94701168645415959931
⋅
10
11
⋅
x
−
20
1
+
7.46437068161927678031
⋅
10
2
⋅
x
−
2
+
1.97865247031583951450
⋅
10
5
⋅
x
−
4
+
2.41535670165126845144
⋅
10
7
⋅
x
−
6
+
1.47478952192985464958
⋅
10
9
⋅
x
−
8
+
4.58595115847765779830
⋅
10
10
⋅
x
−
10
+
7.08501308149515401563
⋅
10
11
⋅
x
−
12
+
5.06084464593475076774
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
14
+
1.43468549171581016479
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
16
+
1.11535493509914254097
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
18
)
g
(
x
)
≈
1
x
2
⋅
(
1
+
8.1359520115168615
⋅
10
2
⋅
x
−
2
+
2.35239181626478200
⋅
10
5
⋅
x
−
4
+
3.12557570795778731
⋅
10
7
⋅
x
−
6
+
2.06297595146763354
⋅
10
9
⋅
x
−
8
+
6.83052205423625007
⋅
10
10
⋅
x
−
10
+
1.09049528450362786
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
12
+
7.57664583257834349
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
14
+
1.81004487464664575
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
16
+
6.43291613143049485
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
18
−
1.36517137670871689
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
20
1
+
8.19595201151451564
⋅
10
2
⋅
x
−
2
+
2.40036752835578777
⋅
10
5
⋅
x
−
4
+
3.26026661647090822
⋅
10
7
⋅
x
−
6
+
2.23355543278099360
⋅
10
9
⋅
x
−
8
+
7.87465017341829930
⋅
10
10
⋅
x
−
10
+
1.39866710696414565
⋅
10
12
⋅
x
−
12
+
1.17164723371736605
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
14
+
4.01839087307656620
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
16
+
3.99653257887490811
⋅
10
13
⋅
x
−
18
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{array}{rcl}f(x)&\approx &{\dfrac {1}{x}}\cdot \left({\frac {\begin{array}{l}1+7.44437068161936700618\cdot 10^{2}\cdot x^{-2}+1.96396372895146869801\cdot 10^{5}\cdot x^{-4}+2.37750310125431834034\cdot 10^{7}\cdot x^{-6}\\~~~+1.43073403821274636888\cdot 10^{9}\cdot x^{-8}+4.33736238870432522765\cdot 10^{10}\cdot x^{-10}+6.40533830574022022911\cdot 10^{11}\cdot x^{-12}\\~~~+4.20968180571076940208\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-14}+1.00795182980368574617\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-16}+4.94816688199951963482\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-18}\\~~~-4.94701168645415959931\cdot 10^{11}\cdot x^{-20}\end{array}}{\begin{array}{l}1+7.46437068161927678031\cdot 10^{2}\cdot x^{-2}+1.97865247031583951450\cdot 10^{5}\cdot x^{-4}+2.41535670165126845144\cdot 10^{7}\cdot x^{-6}\\~~~+1.47478952192985464958\cdot 10^{9}\cdot x^{-8}+4.58595115847765779830\cdot 10^{10}\cdot x^{-10}+7.08501308149515401563\cdot 10^{11}\cdot x^{-12}\\~~~+5.06084464593475076774\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-14}+1.43468549171581016479\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-16}+1.11535493509914254097\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-18}\end{array}}}\right)\\&&\\g(x)&\approx &{\dfrac {1}{x^{2}}}\cdot \left({\frac {\begin{array}{l}1+8.1359520115168615\cdot 10^{2}\cdot x^{-2}+2.35239181626478200\cdot 10^{5}\cdot x^{-4}+3.12557570795778731\cdot 10^{7}\cdot x^{-6}\\~~~+2.06297595146763354\cdot 10^{9}\cdot x^{-8}+6.83052205423625007\cdot 10^{10}\cdot x^{-10}+1.09049528450362786\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-12}\\~~~+7.57664583257834349\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-14}+1.81004487464664575\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-16}+6.43291613143049485\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-18}\\~~~-1.36517137670871689\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-20}\end{array}}{\begin{array}{l}1+8.19595201151451564\cdot 10^{2}\cdot x^{-2}+2.40036752835578777\cdot 10^{5}\cdot x^{-4}+3.26026661647090822\cdot 10^{7}\cdot x^{-6}\\~~~+2.23355543278099360\cdot 10^{9}\cdot x^{-8}+7.87465017341829930\cdot 10^{10}\cdot x^{-10}+1.39866710696414565\cdot 10^{12}\cdot x^{-12}\\~~~+1.17164723371736605\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-14}+4.01839087307656620\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-16}+3.99653257887490811\cdot 10^{13}\cdot x^{-18}\end{array}}}\right)\\\end{array}}}
Mathar, R.J. (2009). "Numerical evaluation of the oscillatory integral over exp(iπx )·x 1/x between 1 and ∞". Appendix B. arXiv :0912.3844 math.CA ]. Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. (2007). "Section 6.8.2 – Cosine and Sine Integrals" . Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (3rd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88068-8 Sloughter, Dan. "Sine Integral Taylor series proof" (PDF) . Difference Equations to Differential Equations . Temme, N.M. (2010), "Exponential, Logarithmic, Sine, and Cosine Integrals" , in Olver, Frank W. J. ; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W. (eds.), NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5 MR 2723248
























![{\displaystyle {\begin{array}{rcl}f(x)&\equiv &\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {\sin(t)}{t+x}}\,dt&=&\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {e^{-xt}}{t^{2}+1}}\,dt&=&\operatorname {Ci} (x)\sin(x)+\left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\cos(x)~,\\g(x)&\equiv &\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {\cos(t)}{t+x}}\,dt&=&\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {te^{-xt}}{t^{2}+1}}\,dt&=&-\operatorname {Ci} (x)\cos(x)+\left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\sin(x)~.\end{array}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d2b43b57fdff2c9f86d9685bbf1d8a0eb7b30c11)














![{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{\infty }e^{iax}{\frac {\ln x}{x^{2}}}\,dx=1+ia\left[-{\frac {\pi ^{2}}{24}}+\gamma \left({\frac {\gamma }{2}}+\ln a-1\right)+{\frac {\ln ^{2}a}{2}}-\ln a+1\right]+{\frac {\pi a}{2}}{\Bigl (}\gamma +\ln a-1{\Bigr )}+\sum _{n\geq 1}{\frac {(ia)^{n+1}}{(n+1)!n^{2}}}~.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/61671b32bbb8068361dfa5d582a6d6f3230a43cf)





![{\displaystyle f(x)\equiv \left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\cos(x)+\operatorname {Ci} (x)\sin(x)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2a843910ab6cb92c362e68ac401c28c1e7cda148)
![{\displaystyle g(x)\equiv \left[{\frac {\pi }{2}}-\operatorname {Si} (x)\right]\sin(x)-\operatorname {Ci} (x)\cos(x)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5f74128afc0519376e13432f0e9f5b0bf6627de7)

